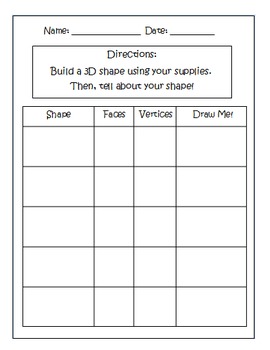
We then create a new Tk window and give it the name '3D Graphics'. Finally we create a canvas in that window, on which we can draw our shapes. If we look at a 3D coordinate, it has the shape. Right click it Hit Format Shape. 3D Format open the top bevel drop down and select Circle. This adds a round bevel to the edge of the circle, and by increasing the width and height (and keeping them equal) the bevel meets in the middle, making a hemisphere. Fill the circle with a decent colour to make the 3D. GeoGebra - Free Online Geometry Tool. Geogebra is the best online geometry software for creating different geometric figures - points, lines, angles, triangles, polygons, circles, elipses, 3D planes, pyramids, cones, spheres. Jun 15, 2016 Exploring the properties of three dimensional shapes is fun for all ages! Because kids are introduced to 3D shapes early on, you could make these together with young kids, or you could use them with high schoolers to explore more complex math. No matter how you use them, this set of foldable 3D shapes is bound to be a hit!
- Create 3d Shapes In Photoshop
- Create 3d Shapes Out Of Paper
- Create 3d Shapes In Inkscape
- Patterns To Make 3d Shapes
Photoshop can build a variety of basic 3D objects using 2D layers as a starting point. After creating a 3D object, you can move it in 3D space, change render settings, add lighting, or merge it with other 3D layers.
Convert 2D layers into 3D postcards (planes with 3D properties). If your starting layer is a text layer, any transparency is retained.
Wrap a 2D layer around a 3D object, such as a cone, cube, or cylinder. War thunder war overlay cracked.
Create a 3D mesh from the grayscale information in a 2D image.
Simulate a metalworking technique called repoussé by extruding a 2D object in 3D space. See Create 3D repoussé.
Build a 3D volume from a multi-frame file such as a DICOM medical imaging file. Photoshop combines the individual slices of the file into a 3D object that you can manipulate in 3D space and view from any angle. You can apply various 3D volume render effects to optimize the display of various materials in the scan, such as bone or soft tissue. See Create a 3D volume.
Note:
You can add a 3D postcard to an existing3D scene to create a surface that displays shadows and reflectionsfrom other objects in the scene.
Open a 2D image and select the layer you want to convertto a postcard.
The 2D layer is converted to a 3D layer in the Layers panel. The 2D layer content is applied as a material to both sides of the postcard.
The original 2D layer appears in the Layers panel as the Diffuse texture map for the 3D postcard object. (See 3D panel overview.)
The 3D layer retains the dimensions of the original 2D image.
(Optional) To add the 3D postcard as a surface plane to a 3D scene, merge the new 3D layer with an existing 3D layer containing other 3D objects, then align it as necessary. (See Combine 3D objects.)
To retain the new 3D content, export the 3D layer in a 3D file format or save it in PSD format. (See Export 3D layers.)
Depending on the object type you choose, the resulting3D model can contain one or more meshes. The Spherical Panoramaoption maps a panoramic image inside a 3D sphere.
Open a 2D image and select the layer that you want toconvert to a 3D shape.
Choose 3D > New Shape From Layer, and select a shape fromthe menu. Shapes include single-mesh objects like a donut, sphere,or hat, as well as multiple mesh objects such as a cone, cube, cylinder,soda can, or wine bottle.
Note:
You can add your own customshapes to the shape menu. Shapes are Collada (.dae) 3D model files.To add a shape, place the Collada model file in the PresetsMeshesfolder inside the Photoshop program folder.
The 2D layer is converted to a 3D layer in the Layers panel.
The original 2D layer appears in the Layers panel as a Diffuse texture map. It may be used on one or more surfaces of the new 3D object. Other surfaces may be assigned a default diffuse texture map with a default color setting. See 3D panel overview.
(Optional) Use the Spherical Panorama option if you are using a panoramic image as your 2D input. This option converts a complete 360 x 180 degree spherical panorama to a 3D layer. Once converted to a 3D object, you can paint areas of the panorama that are typically difficult to reach, such as the poles or areas containing straight lines. For information on creating a 2D panorama by stitching images together, see Create 360 degree panoramas.
Export the 3D layer in a 3D file format or save in PSD format to retain the new 3D content. See Export 3D layers.
The New Mesh from Grayscale command converts a grayscaleimage into a depth map, which translates lightness values into asurface of varying depth. Lighter values create raised areas inthe surface, darker values create lower areas. Photoshop then appliesthe depth map to one of four possible geometries to create a 3Dmodel.
Open a 2D image and select one or more layers that youwant to convert to a 3D mesh.
(Optional) Convert the image to grayscale mode. (Choose Image> Mode > Grayscale, or use Image > Adjustments > Black& White to fine-tune the grayscale conversion.
Note:
Ifyou use an RGB image as input when creating a mesh, the green channel isused to generate the depth map.
(Optional) Make adjustments to the grayscale image if necessaryto limit the range of lightness values.
Choose 3D > New Mesh From Grayscale, and then select amesh option.
Applies depth map data to a planar surface.
Creates two planes reflected along a central axis and appliesdepth map data to both planes.
Applies depth map data outward from the center of a verticalaxis.
Applies depth map data radially outward from a center point.
Photoshop creates a 3D layer containing the new mesh. It alsocreates Diffuse, Opacity, and Planar Depth Map texture maps forthe 3D object, using the original grayscale or color layer.
You can reopen the Planar Depth Map as a Smart Object at anytime and edit it. When you save it, the mesh is regenerated.
Note:
The Opacity texture map does not appear in the Layers panel,because that map uses the same texture file as the Diffuse map (theoriginal 2D layer). When two texture maps reference the same file,the file appears only once in the Layers panel.
Usingthe Photoshop Animation timeline, you can create 3D animations that movea 3D model through space and change the way it displays over time.You can animate any of the following properties of a 3D layer:
3D object or camera position. Use the 3D position orcamera tools to move the model or 3D camera over time. Photoshopcan tween frames between position or camera movements to createsmooth motion effects.
3D render settings. Change render modes, with the abilityto tween transitions between some render modes. For example, changeVertices mode gradually to Wireframe over time, to simulate thesketching-in of a model's structure.
3D cross section. Rotate an intersecting plane to displaya changing cross section over time. Change cross section settingsbetween frames to highlight different model areas during an animation.
For high quality animations, you can render each animation frame using the Render for Final Output render setting. See Change rendering effects.
More like this
- JavaFX Tutorial
- JavaFX Useful Resources
- Selected Reading
In the earlier chapters, we have seen how to draw 2D shapes on an XY plane. In addition to these 2D shapes, we can draw several other 3D shapes as well using JavaFX.
3D Shape
In general, a 3D shape is a geometrical figure that can be drawn on the XYZ plane. These include a Cylinder, Sphere and a Box.
Each of the above mentioned 3D shape is represented by a class and all these classes belong to the package javafx.scene.shape. The class named Shape3D is the base class of all the 3-Dimensional shapes in JavaFX.
Creating a 3D Shape
To create a 3-Dimensional shape, you need to −
Instantiate the respective class of the required 3D shape.
Set the properties of the 3D shape.
Add the 3D shape object to the group.
Instantiating the Respective Class
To create a 3-Dimensional shape, first of all you need to instantiate its respective class. For example, if you want to create a 3D box, you need to instantiate the class named Box as follows −
Setting the Properties of the Shape
After instantiating the class, you need to set the properties for the shape using the setter methods.
For example, to draw a 3D box you need to pass its Width, Height, Depth. You can specify these values using their respective setter methods as follows −

Adding the Shape Object to the Group
Finally, you need to add the object of the shape to the group by passing it as a parameter of the constructor as shown below.
The following table gives you the list of various 3D shapes provided by JavaFX. Visual nastran 4d 2004 crack.
| S.No | Shape & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Box A cuboid is a three-dimensional shape with a length (depth), width, and a height. In JavaFX a three-dimensional box is represented by a class named Box. This class belongs to the package javafx.scene.shape. By instantiating this class, you can create a Box node in JavaFX. This class has 3 properties of the double datatype namely −
|
| 2 | Cylinder A cylinder is a closed solid that has two parallel (mostly circular) bases connected by a curved surface. It is described by two parameters, namely, the radius of its circular base and the height of the cylinder. In JavaFX, a cylinder is represented by a class named Cylinder. This class belongs to the package javafx.scene.shape. By instantiating this class, you can create a cylinder node in JavaFX. This class has 2 properties of the double datatype namely −
|
| 3 | Sphere A sphere is defined as the set of points that are all at the same distance r from a given point in a 3D space. This distance r is the radius of the sphere and the given point is the centre of the sphere. In JavaFX, a sphere is represented by a class named Sphere. This class belongs to the package javafx.scene.shape. By instantiating this class, you can create a sphere node in JavaFX. This class has a property named radius of double datatype. It represents the radius of a Sphere. |
Properties of 3D Objects
For all the 3 Dimensional objects, you can set various properties like Cull Face, Drawing Mode, Material.
The following section discusses the properties of 3D objects.
Cull Face
In general, culling is the removal of improperly oriented parts of a shape (which are not visible in the view area).
The Cull Face property is of the type CullFace and it represents the Cull Face of a 3D shape. You can set the Cull Face of a shape using the method setCullFace() as shown below −
The stroke type of a shape can be −
None − No culling is performed (CullFace.NONE).
Front − All the front facing polygons are culled. (CullFace.FRONT).
Back − All the back facing polygons are culled. (StrokeType.BACK).
By default, the cull face of a 3-Dimensional shape is Back.
Example
The following program is an example which demonstrates various cull faces of the sphere. Save this code in a file with the name SphereCullFace.java.
Compile and execute the saved Java file from the command prompt using the following commands.
Create 3d Shapes In Photoshop
On executing, the above program generates a JavaFX window displaying three spheres with cull face values FRONT, BACK and NONE respectively as follows −
Drawing Modes
It is the property is of the type DrawMode and it represents the drawing mode used to draw the current 3D shape. You can choose the draw mode to draw a 3D shape using the method setDrawMode () as follows −
In JavaFX, you can choose two draw modes to draw a 3D shape, which are −
Bcs classification system database. This approach is repeated such that at each inflection point, data is gathered to support the development plan.

Fill − This mode draws and fills a 2D shape (DrawMode.FILL).
Line − This mode draws a 3D shape using lines (DrawMode.LINE).
By default, the drawing mode of a 3Dimensional shape is fill.
Example
The following program is an example which demonstrates various draw modes of a 3D box. Save this code in a file with the name BoxDrawMode.java.
Create 3d Shapes Out Of Paper
Compile and execute the saved java file from the command prompt using the following commands.
On executing, the above program generates a JavaFX window displaying two boxes with draw mode values LINE and FILL respectively, as follows −
Material
The cull Face property is of the type Material and it is used to choose the surface of the material of a 3D shape. You can set the material of a 3D shape using the method setCullFace() as follows −
As mentioned above for this method, you need to pass an object of the type Material. The PhongMaterial class of the package javafx.scene.paint is a sub class of this class and provides 7 properties that represent a Phong shaded material. You can apply all these type of materials to the surface of a 3D shape using the setter methods of these properties.
Following are the type of materials that are available in JavaFX −
bumpMap − This represents a normal map stored as a RGB Image.
diffuseMap − This represents a diffuse map.
selfIlluminationMap − This represents a self-illumination map of this PhongMaterial.
specularMap − This represents a specular map of this PhongMaterial.
diffuseColor − This represents a diffuse color of this PhongMaterial.
specularColor − This represents a specular color of this PhongMaterial.
specularPower − This represents a specular power of this PhongMaterial.
By default, the material of a 3-Dimensional shape is a PhongMaterial with a diffuse color of light gray.
Example
Following is an example which displays various materials on the cylinder. Save this code in a file with the name CylinderMaterials.java.
Compile and execute the saved java file from the command prompt using the following commands.
Create 3d Shapes In Inkscape

Adding the Shape Object to the Group
Finally, you need to add the object of the shape to the group by passing it as a parameter of the constructor as shown below.
The following table gives you the list of various 3D shapes provided by JavaFX. Visual nastran 4d 2004 crack.
| S.No | Shape & Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Box A cuboid is a three-dimensional shape with a length (depth), width, and a height. In JavaFX a three-dimensional box is represented by a class named Box. This class belongs to the package javafx.scene.shape. By instantiating this class, you can create a Box node in JavaFX. This class has 3 properties of the double datatype namely −
|
| 2 | Cylinder A cylinder is a closed solid that has two parallel (mostly circular) bases connected by a curved surface. It is described by two parameters, namely, the radius of its circular base and the height of the cylinder. In JavaFX, a cylinder is represented by a class named Cylinder. This class belongs to the package javafx.scene.shape. By instantiating this class, you can create a cylinder node in JavaFX. This class has 2 properties of the double datatype namely −
|
| 3 | Sphere A sphere is defined as the set of points that are all at the same distance r from a given point in a 3D space. This distance r is the radius of the sphere and the given point is the centre of the sphere. In JavaFX, a sphere is represented by a class named Sphere. This class belongs to the package javafx.scene.shape. By instantiating this class, you can create a sphere node in JavaFX. This class has a property named radius of double datatype. It represents the radius of a Sphere. |
Properties of 3D Objects
For all the 3 Dimensional objects, you can set various properties like Cull Face, Drawing Mode, Material.
The following section discusses the properties of 3D objects.
Cull Face
In general, culling is the removal of improperly oriented parts of a shape (which are not visible in the view area).
The Cull Face property is of the type CullFace and it represents the Cull Face of a 3D shape. You can set the Cull Face of a shape using the method setCullFace() as shown below −
The stroke type of a shape can be −
None − No culling is performed (CullFace.NONE).
Front − All the front facing polygons are culled. (CullFace.FRONT).
Back − All the back facing polygons are culled. (StrokeType.BACK).
By default, the cull face of a 3-Dimensional shape is Back.
Example
The following program is an example which demonstrates various cull faces of the sphere. Save this code in a file with the name SphereCullFace.java.
Compile and execute the saved Java file from the command prompt using the following commands.
Create 3d Shapes In Photoshop
On executing, the above program generates a JavaFX window displaying three spheres with cull face values FRONT, BACK and NONE respectively as follows −
Drawing Modes
It is the property is of the type DrawMode and it represents the drawing mode used to draw the current 3D shape. You can choose the draw mode to draw a 3D shape using the method setDrawMode () as follows −
In JavaFX, you can choose two draw modes to draw a 3D shape, which are −
Bcs classification system database. This approach is repeated such that at each inflection point, data is gathered to support the development plan.
Fill − This mode draws and fills a 2D shape (DrawMode.FILL).
Line − This mode draws a 3D shape using lines (DrawMode.LINE).
By default, the drawing mode of a 3Dimensional shape is fill.
Example
The following program is an example which demonstrates various draw modes of a 3D box. Save this code in a file with the name BoxDrawMode.java.
Create 3d Shapes Out Of Paper
Compile and execute the saved java file from the command prompt using the following commands.
On executing, the above program generates a JavaFX window displaying two boxes with draw mode values LINE and FILL respectively, as follows −
Material
The cull Face property is of the type Material and it is used to choose the surface of the material of a 3D shape. You can set the material of a 3D shape using the method setCullFace() as follows −
As mentioned above for this method, you need to pass an object of the type Material. The PhongMaterial class of the package javafx.scene.paint is a sub class of this class and provides 7 properties that represent a Phong shaded material. You can apply all these type of materials to the surface of a 3D shape using the setter methods of these properties.
Following are the type of materials that are available in JavaFX −
bumpMap − This represents a normal map stored as a RGB Image.
diffuseMap − This represents a diffuse map.
selfIlluminationMap − This represents a self-illumination map of this PhongMaterial.
specularMap − This represents a specular map of this PhongMaterial.
diffuseColor − This represents a diffuse color of this PhongMaterial.
specularColor − This represents a specular color of this PhongMaterial.
specularPower − This represents a specular power of this PhongMaterial.
By default, the material of a 3-Dimensional shape is a PhongMaterial with a diffuse color of light gray.
Example
Following is an example which displays various materials on the cylinder. Save this code in a file with the name CylinderMaterials.java.
Compile and execute the saved java file from the command prompt using the following commands.
Create 3d Shapes In Inkscape
Patterns To Make 3d Shapes
On executing, the above program generates a JavaFX window displaying 7 cylinders with Materials, Bump Map, Diffuse Map, Self-Illumination Map, Specular Map, Diffuse Color, Specular Color, (BLANCHEDALMOND) Specular Power, respectively, as shown in the following screenshot −
